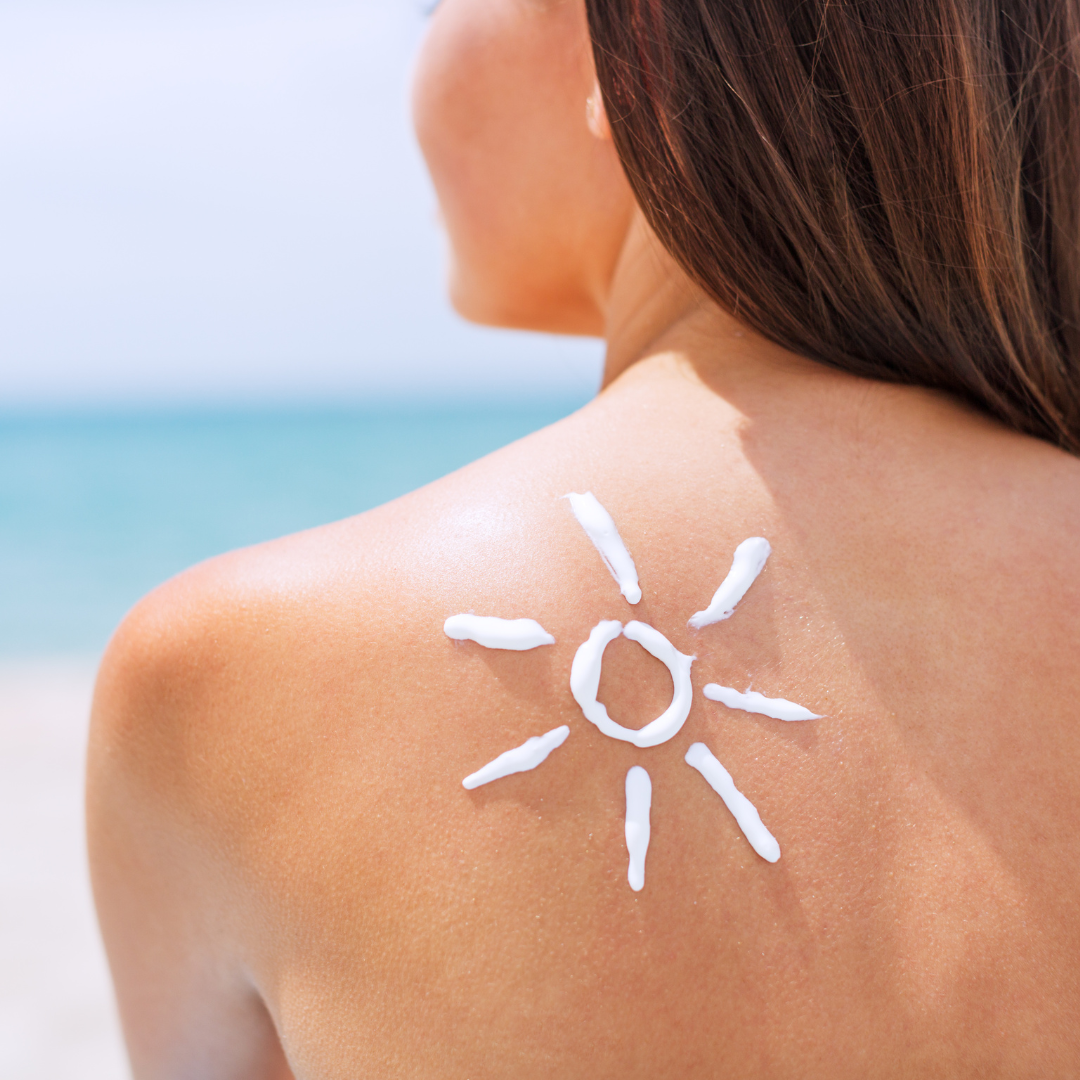
We always hear about UV rays and how harmful they are, especially around this time of year but what exactly are they and how do they affect the skin? Does this mean that we should avoid the sun altogether? July is the peak of the summer season and also the month most of us do outdoor activities and so fittingly, it is also UV awareness month. Here is some crucial information on what UV rays are and how we can protect our skin by limiting exposure, including the best SPF moisturizer for the face.
What are UV rays?
Simply put, UV (Ultra-violet) radiation is a part of the natural energy produced by the sun. UV rays have shorter wavelengths than visible light, so we are unable to see them but our skin can certainly feel them and be affected by them.
How do UV rays affect our skin?
UV rays activate a chemical in the skin called melanin. Melanin is the first defense and will absorb most, but not all the UV rays. While this is being done, you will get a tan. A tan is a sign that your skin is trying to keep UV rays from damaging your skin.
Melanin does a good job of absorbing the rays but since it is impossible to absorb all, it is not advisable to spend a lot of time in the sun or you will be at risk for sunburn. A sunburn happens when the amount of UV rays exceeds the protection that the skin's melanin can provide.
Types of UV rays
There are 3 types of UV rays:
- UV-A. These rays go into the skin more deeply than UVB rays. They play a major part in skin aging and wrinkling. They also cause skin cell damage that can lead to cancer.
- UV-B. These rays are the main cause of sunburn. They tend to damage the skin's outer layers. Exposure to these rays is linked to most skin cancers.
- UV-C. These are dangerous rays, but they don’t reach our skin. Luckily, the Earth’s atmosphere absorbs UV-C rays before they reach us.
Conditions linked to over-exposure to UV rays
-
Premature aging of the skin. This is also called photoaging. It causes the skin to become thick and leathery over time. Other signs of photoaging include earlier-than-normal freckling, wrinkling, loss of collagen, and widening of small blood vessels in the skin. These changes can happen at younger ages and more quickly in people who regularly spend a lot of time in the sun or regularly use tanning beds or lamps. The skin may also develop brown spots (liver spots) in later years.
-
Suppression of immunity which often leads to skin cancer. When UV radiation suppresses immune responses, the body's ability to fight certain diseases, including skin cancer, is reduced. It is suspected that overexposure to UV radiation also interferes with the effectiveness of immunizations given through the skin.
-
Cataracts and other eye disorders. Cataracts, an eye disorder characterized by a change in the structure of the crystalline lens that causes blurred vision, are a leading cause of blindness around the world - and excessive UV exposure is one of the risk factors in the development of cataracts.
Staying safe in the sun while still having fun
Remember that the sun is an excellent source of Vitamin D, so some exposure is necessary. Here are some tips to keep you safe this summer while enjoying outdoor activities:- Limit your time spent in the sun, especially during the hours 10 am-2 pm. Seek shaded areas, especially in this time frame.
- Wear sunglasses with UV protection.
- Take extra care around sand, and water. They all reflect UV rays and give you more exposure.
- Protect your skin with clothing and sunscreen. Apply sunscreen with at least SPF 30 every 2 hours, such as Best SPF Moisturizer for Face even on cloudy days.
- Your daily AM routine should include a serum that addresses UV damage, such as the Dp Dermaceuticals Antioxidant Cocktail which has potent Vitamin C to neutralize damaging free radicals.